The Digital Bridge: How Fintech is Revolutionizing Financial Inclusion
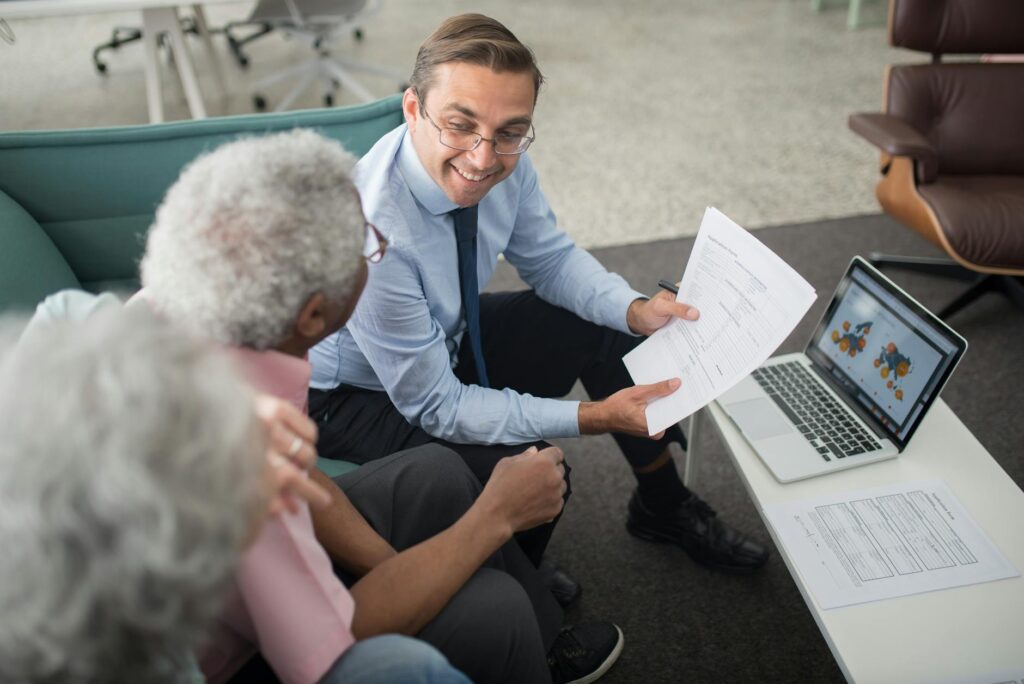
Financial inclusion represents one of the most powerful levers for economic empowerment and poverty alleviation in the 21st century. For decades, vast segments of the global population, particularly in emerging economies, have been locked out of the formal financial system, unable to access basic services like savings accounts, credit, and insurance. This exclusion has stifled entrepreneurship, limited economic resilience, and perpetuated cycles of poverty. Today, a seismic shift is underway, driven by the innovative force of financial technology. Fintech is not merely tweaking the existing system; it is fundamentally rebuilding it from the ground up to be more accessible, affordable, and relevant to the needs of the underserved.
The Unbanked Challenge and the Fintech Opportunity
The scale of the challenge is immense. In Africa alone, approximately 50% of the population remains unbanked or underbanked, representing a massive, untapped market with a potential value of over $2.7 billion for digital financial solutions. Traditional banks, with their brick-and-mortar branches, high fees, and stringent documentation requirements, have historically failed to reach these individuals. The barriers are multifaceted: geographical remoteness, lack of formal identification, irregular income streams, and a pervasive distrust of traditional financial institutions.
This is where fintech services have stepped in, acting as a powerful catalyst for change. By leveraging ubiquitous mobile technology, fintech companies are bypassing traditional infrastructure. A simple smartphone or even a basic feature phone becomes a digital bank branch, payment terminal, and loan officer, all in the palm of the user’s hand. This mobile-first approach is the cornerstone of the new inclusion paradigm, dismantling the physical and bureaucratic barriers that have excluded millions.
Key Drivers Powering Inclusive Fintech Solutions
Several converging trends are accelerating the pace of financial inclusion through technology.
1. Hyper-Personalization and AI-Driven Accessibility
The future of finance is not one-size-fits-all; it is hyper-personalized. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are at the forefront of this transformation. For instance, companies like M-Kopa are using AI to analyze alternative data—such as mobile phone usage patterns—to create credit scores for individuals with no formal financial history. This allows them to offer “pay-as-you-go” financing for essential assets like solar home systems and smartphones, a service unimaginable through traditional banking channels. AI is also powering sophisticated fraud detection and delivering personalized financial advice, making digital finance both smarter and safer for new entrants.
2. The Rise of Embedded Finance
Financial services are becoming invisible, seamlessly woven into the fabric of everyday life through embedded finance. This model integrates payments, lending, and insurance directly into non-financial platforms, such as agricultural apps, ride-hailing services, and e-commerce marketplaces. A farmer can now secure a loan for seeds within their agritech app, and a small merchant can receive instant payment for a sale through a point-of-sale system integrated with a digital wallet. Projected to grow at a staggering 45.3% annually in Africa, embedded finance makes accessing capital and making transactions a natural byproduct of daily activities, rather than a separate, daunting task.
3. Streamlining Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
For many in developing nations, remittances from family members abroad are a critical lifeline. However, traditional money transfer operators are often slow and exorbitantly expensive. Fintech startups like Chipper Cash, NALA, and MFS Africa are leveraging blockchain technology and stablecoins to dramatically reduce the cost and time involved in cross-border payments. By offering low-cost remittances, these platforms are putting more money directly into the hands of recipients, boosting local economies and enhancing financial resilience for families.
Navigating the Roadblocks to Universal Access
Despite the remarkable progress, the path to universal financial inclusion is not without its obstacles.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Significant portions of the population still lack reliable internet connectivity or even consistent electricity. While mobile penetration is high, the quality of service can be a barrier. Furthermore, as noted in industry reports, only a handful of African countries have robust, real-time payment systems, creating interoperability challenges.
- Regulatory Fragmentation: The African continent, for example, is a mosaic of different regulatory environments. Variable licensing requirements and compliance rules across borders create complexity for fintechs trying to scale their solutions regionally. Initiatives like the RegTech Africa Conference are crucial for fostering public-private partnerships to harmonize these frameworks.
- The Profitability Puzzle: Serving low-income populations with small transaction values presents a unique business challenge. Customer acquisition costs can be high, and achieving profitability is significantly more difficult than in mature markets. This necessitates innovative, scalable business models that can operate efficiently with thin margins.
The Future is Collaborative and Connected
The future of financial inclusion lies in strategic collaboration. The success of digital banks like TymeBank and TymeBank, which have achieved unicorn status by targeting the underserved, demonstrates the viability of this market. We are also seeing powerful global partnerships, such as Moove’s backing by Uber, which help scale solutions internationally. Furthermore, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) promises to boost intra-African trade, creating a pressing need for the interoperable payment systems that fintechs are uniquely positioned to provide.
In conclusion, the fintech revolution is building a digital bridge to financial inclusion that is stronger and more accessible than ever before. By harnessing mobile technology, data analytics, and innovative business models, fintech services are transforming phones into powerful economic tools. While challenges around infrastructure and regulation remain, the relentless pace of innovation and a growing focus on collaboration suggest a future where finance is not a privilege for the few, but a fundamental utility for all. The journey is far from over, but the direction is clear: forward, and inclusive.








1 Comment
NellMatsen
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you’ve put in writing this website. I’m hoping the same high-grade website post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing skills has encouraged me to get my own site now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings fast. Your write up is a good example of it.